Create shimmer, parallax or other rotation effects based on device orientation.
.motionManager()- A view modifier that adds aMotionManagerclass into the environment.ShimmerView- A color that shimmers with another color as if reflecting light when the device rotates..shimmer()- A view modifier that overlays a shimmer color as if reflecting light when the device rotates..parallax()- A view modifier that moves the view to add a parallax effect when the device rotates.LookingGlass- A view that rotates its child view to a specific 3d angle relative to the real world and positions it relative to the device..deviceRotationEffect()- A view modifier that rotates a view based on device rotation..rotation3dEffect()- A view modifier that rotates a view based on a quaternion.Quat- A wrapper for simd.quaternion with handy extensions.
The Example folder has an app that demonstrates the features of this package.
This package is compatible with iOS 14+.
- In Xcode go to
File -> Add Packages - Paste in the repo's url:
https://github.com/ryanlintott/LookingGlassUIand select by version. - Import the package using
import LookingGlassUI
Really it's up to you. I currently use this package to create a gold shimmer effect on many gold elements in the Old English Wordhord app. Download it for free and turn on the shimmer effect in Settings.
LookingGlassUI is open source and free but if you like using it, please consider supporting my work.
Before adding any custom views, add the .motionManager view modifier once in your app, somewhere in the heirarchy above any other views or modifiers used in this package.
ContentView()
.motionManager(updateInterval: 0.1, disabled: false)Requires .motionManager()
This view acts like Color but a second shimmer color will appear when device is rotated. The effect can be enabled via a parameter or set to only show in dark or light mode. If MotionManager is disabled only the background color will be shown.
ShimmerView(mode: .darkModeOnly, color: .goldShimmer, background: .gold)Requires .motionManager()
Use .shimmer() view modifier if you want to add a default shimmer effect to another SwiftUI View. If MotionManager is disabled the modifier has no effect.
Text("Hello, World!")
.shimmer(color: .gold)Requires .motionManager()
Use .parallax(multiplier: CGFloat, maxOffset: CGFloat) view modifier if you want to add a parallax effect to any SwiftUI View. If MotionManager is disabled the modifier has no effect.
Text("Hello, World!")
.parallax(multiplier: 40, maxOffset: 100)Requires .motionManager()
Use LookingGlass if you want to project any SwiftUI view based on a real-world rotation and create your own custom effect. Content appears as if rotated and positioned from the center of the device regardless of positioin on the screen or if it's in a scrollview. If MotionManager is disabled nothing will be shown.
LookingGlass(.reflection, distance: 4000, perspective: 0, pitch: .degrees(45), yaw: .zero, localRoll: .zero, isShowingInFourDirections: false) {
Text("Hello, World")
.foregroundColor(.white)
.frame(width: 500, height: 500)
.background(Color.red)
}Requires .motionManager()
Use .deviceRotationEffect() if you want to rotate a view based on device rotation. Content is rotated and positioned based on it's own center. If MotionManager is disabled nothing will be shown.
Text("Hello, World")
.foregroundColor(.white)
.frame(width: 500, height: 500)
.background(Color.red)
.deviceRotationEffect(.reflection, distance: 4000, perspective: 0, pitch: .degrees(10), yaw: .zero, localRoll: .zero, isShowingInFourDirections: false)Rotate SwiftUI Views based on quaterions. This ensures a smooth rotation from any point to any other point.
Text("Hello, World")
.rotation3dEffect(quaternion: Quat(pitch: .degrees(45), yaw: .zero, localRoll: .degrees(-30)), anchor: .center, anchorZ: 200, perspective: 0.2)Quat is a wrapper for simd.quaternion with handy parameters like yaw, pitch, and roll and a way to init from pitch, yaw and localRoll.
In window mode a view appears as if your phone is a window looking into a 3d environment.
In reflection mode a view appears as if your phone has a camera pointing out of the screen back at a 3d envrionment. It's not a true reflection as it doesn't take into account the viewer's eye location but it's a useful approximation.
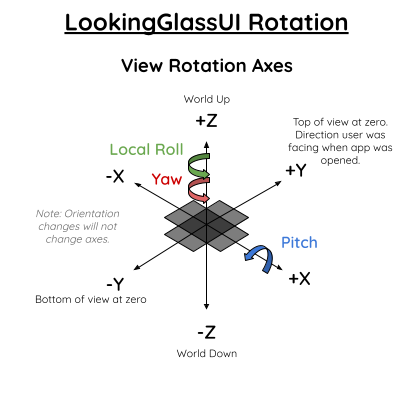
Views are positioned based on a quaternion or pitch, yaw, and local roll angles. All angles at zero means the view will be visible when the phone is flat with the top pointing away from the user. (see diagram below)
- Local Roll rotate the view around the Z axis. 10 degrees will tilt the view counter-clockwise
- Pitch will rotate the view around the X axis. 90 degrees will bring the view up directly in front of the user.
- Yaw will rotate the view around the Z axis again. 5 degrees will move the view slightly to the left of the user. If you set isShowingInFourDirections to true the view will be copied 3 additional times and rotated at -90, 90, and 180 degrees from the position you chose.
- The view is then moved away from the origin based on the distance provided. The direction is dependant on choosing window or reflection.
- As the user moves their device around they will always see your view in the location you've set.
Don't worry about device orientation. Although Core Motion doesn't compensate for this, LookingGlassUI does.
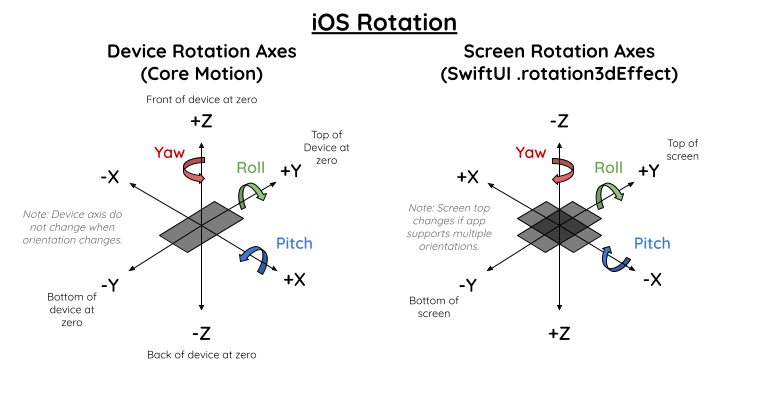
3D space is confusing on iOS, especially as Core Motion and SwiftUI's rotation3dEffect each seem to use different axes. I created this diagram to keep track of how each one works. You probably won't need these unless you want to do something more custom. It's important to note that the Screen Rotation Axes are only used for determining rotation direction using the right hand rule for a rotating body. When translating a view (using .offset or similar), the axes are different with +Y towards the bottom of the screen and +X to the right. These axes are not needed as we only deal with rotation