A lightweight and powerful iOS framework for intercepting HTTP/HTTPS Traffic from your app. No more messing around with proxy, certificate config.
- Automatically intercept all HTTP/HTTPS Traffic with ease
- Capture WS/WSS Traffic from URLSessionWebSocketTask
- Capture gRPC traffic
- ✅ No need to config HTTP Proxy, Install or Trust any Certificate
- Support iOS Physical Devices and Simulators
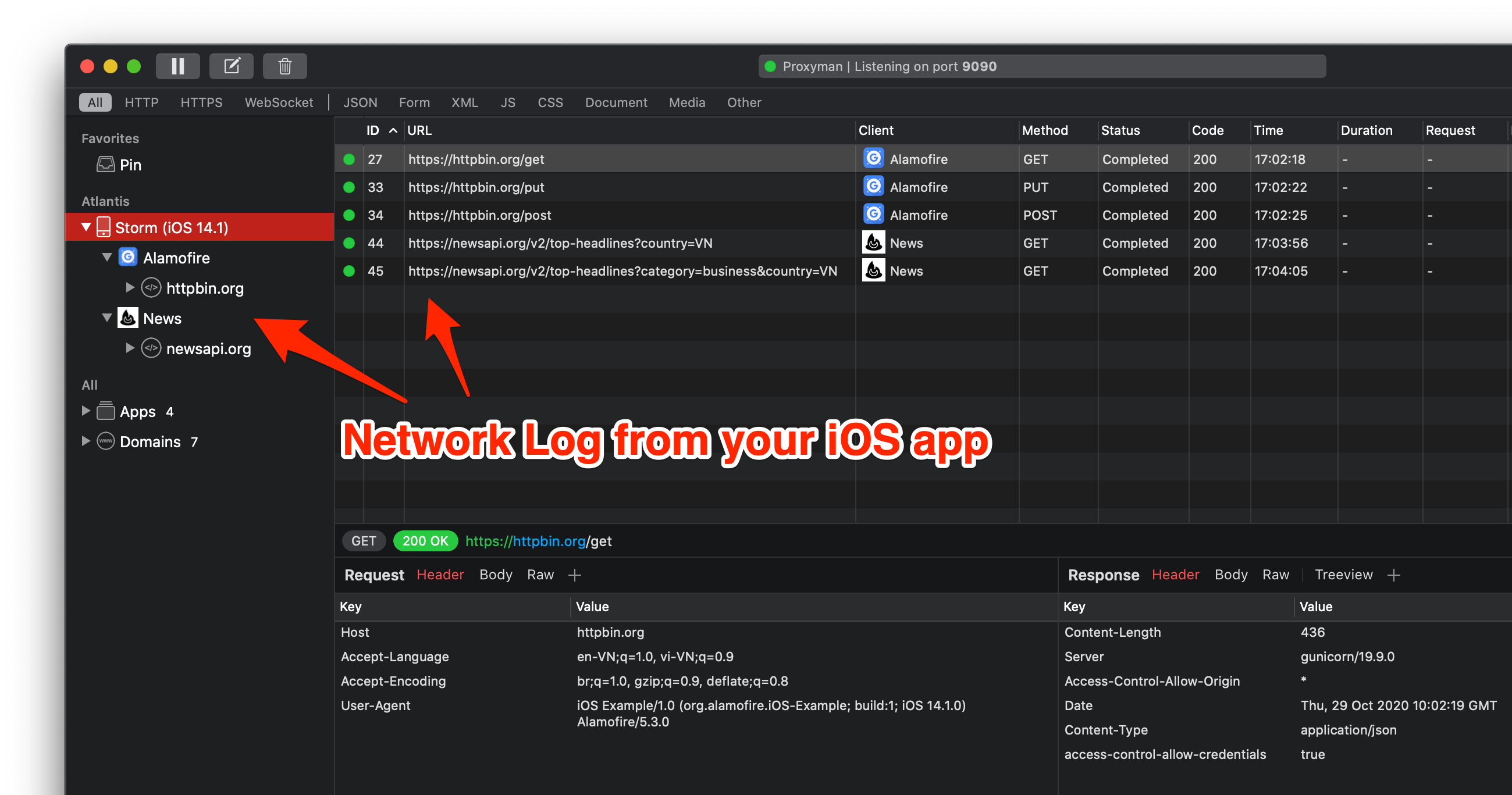
- Review traffic log from macOS Proxyman app (Github)
- Categorize the log by project and devices.
- Only for Traffic Inspector, not for Debugging Tools
- Ready for Production
- macOS Proxyman app
- iOS 13.0+ / macOS 10.15+ / Mac Catalyst 13.0+
- Xcode 11+
- Swift 5.0+
From iOS 14, it's required to add NSLocalNetworkUsageDescription and NSBonjourServices to your info.plist
- Open your
Info.plistfile and add the following keys and values: - Example
<key>NSLocalNetworkUsageDescription</key>
<string>Atlantis would use Bonjour Service to discover Proxyman app from your local network.</string>
<key>NSBonjourServices</key>
<array>
<string>_Proxyman._tcp</string>
</array>- Install Atlantis by CocoaPod or SPM, then start Atlantis
By default, Bonjour service will try to connect all Proxyman app in the same network:
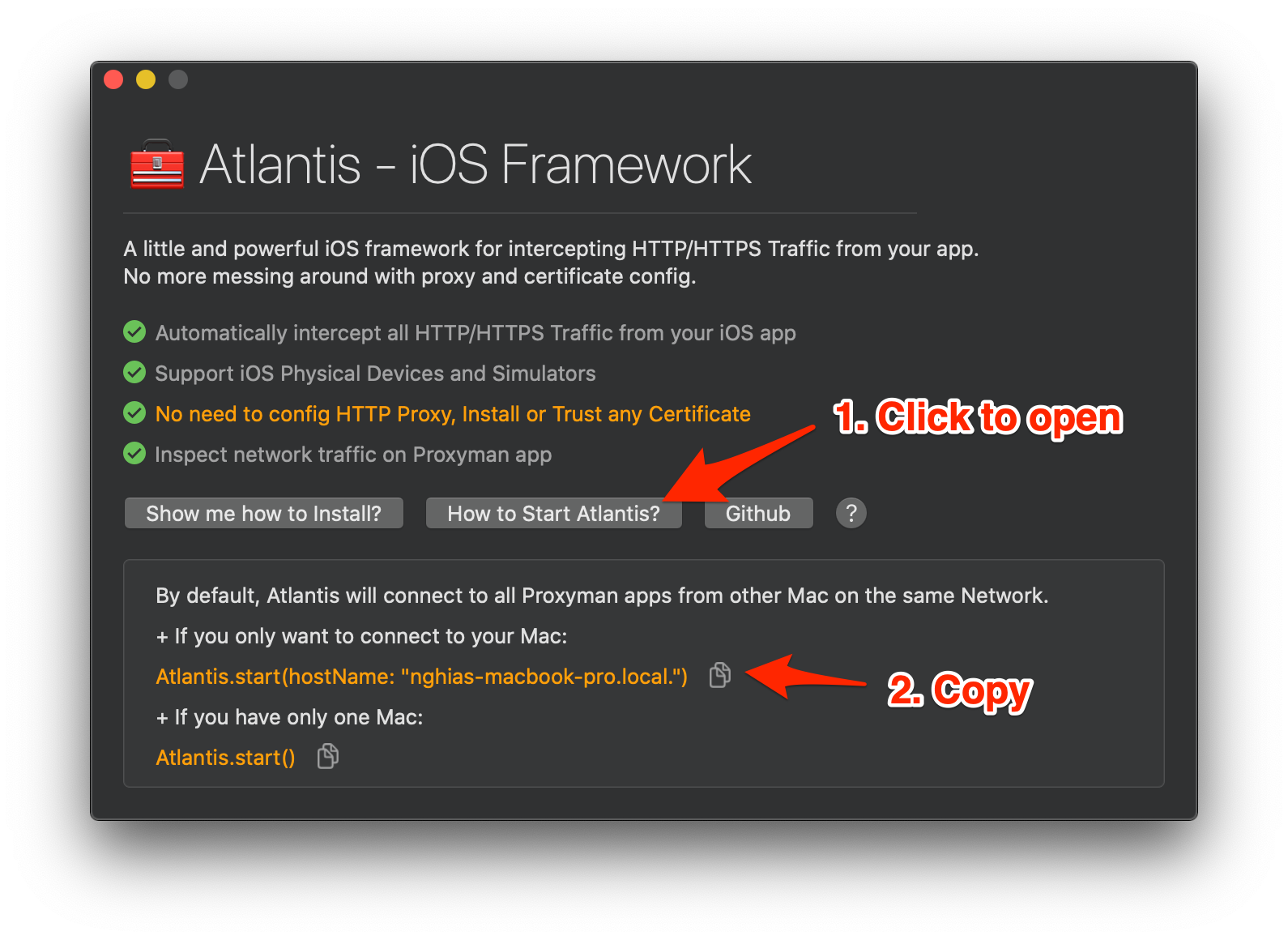
If you have only ONE MacOS machine that has Proxyman. Let's use the simple version:
- Open file
AppDelegate.swift
#if DEBUG
import Atlantis
#endif
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Auto connect to a current Macbook
// Add to the end of `application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` in AppDelegate.swift or SceneDelegate.swift
#if DEBUG
Atlantis.start()
#endif
return true
}- If there are many Proxyman apps from colleagues' Mac Machines, and you would Atlantis connects to your macOS machine. Let use
Atlantis.start(hostName:)version
#if DEBUG
import Atlantis
#endif
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Auto connect to a current Macbook
// Add to the end of `application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` in AppDelegate.swift or SceneDelegate.swift
#if DEBUG
Atlantis.start(hostName: "Your_host_name")
#endif
return true
}You can get the hostName from Proxyman -> Certificate menu -> Install for iOS -> Atlantis -> How to Start Atlantis -> and copy the HostName
- If your project uses Objective-C, please use CocoaPod to install Atlantis (Install via SPM might not work).
#import "Atlantis-Swift.h"
// Or import Atlantis as a module, you can use:
@import Atlantis;
// Add to the end of `application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)` in AppDelegate
[Atlantis startWithHostName:nil];- Make sure your iOS devices/simulator and macOS Proxyman are in the same Wi-Fi network or connect your iOS Devices to your Mac by a USB cable
- Open macOS Proxyman (or download the lasted here)
- Open your iOS app and Inspect traffic logs from Proxyman app
- Enjoy debugging ❤️
- Add the following line to your Podfile
pod 'atlantis-proxyman'- Add
https://github.com/ProxymanApp/atlantisto your project by: Open Xcode -> File Menu -> Swift Packages -> Add Package Dependency...
- Add to your Cartfile
github "ProxymanApp/atlantis"
- Run
carthage update --use-xcframeworks - Drag Atlantis.framework from your project
- Create a Carthage Script as the Carthage guideline
For Carthage with Xcode 12, please check out the workaround: https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage/blob/master/Documentation/Xcode12Workaround.md
From Atlantis 1.9.0+, Atlantis is capable of capturing all WS/WSS Traffic, which is made by URLSessionWebSocketTask, and send to Proxyman app. You don't need to config anything, it works out of the box.
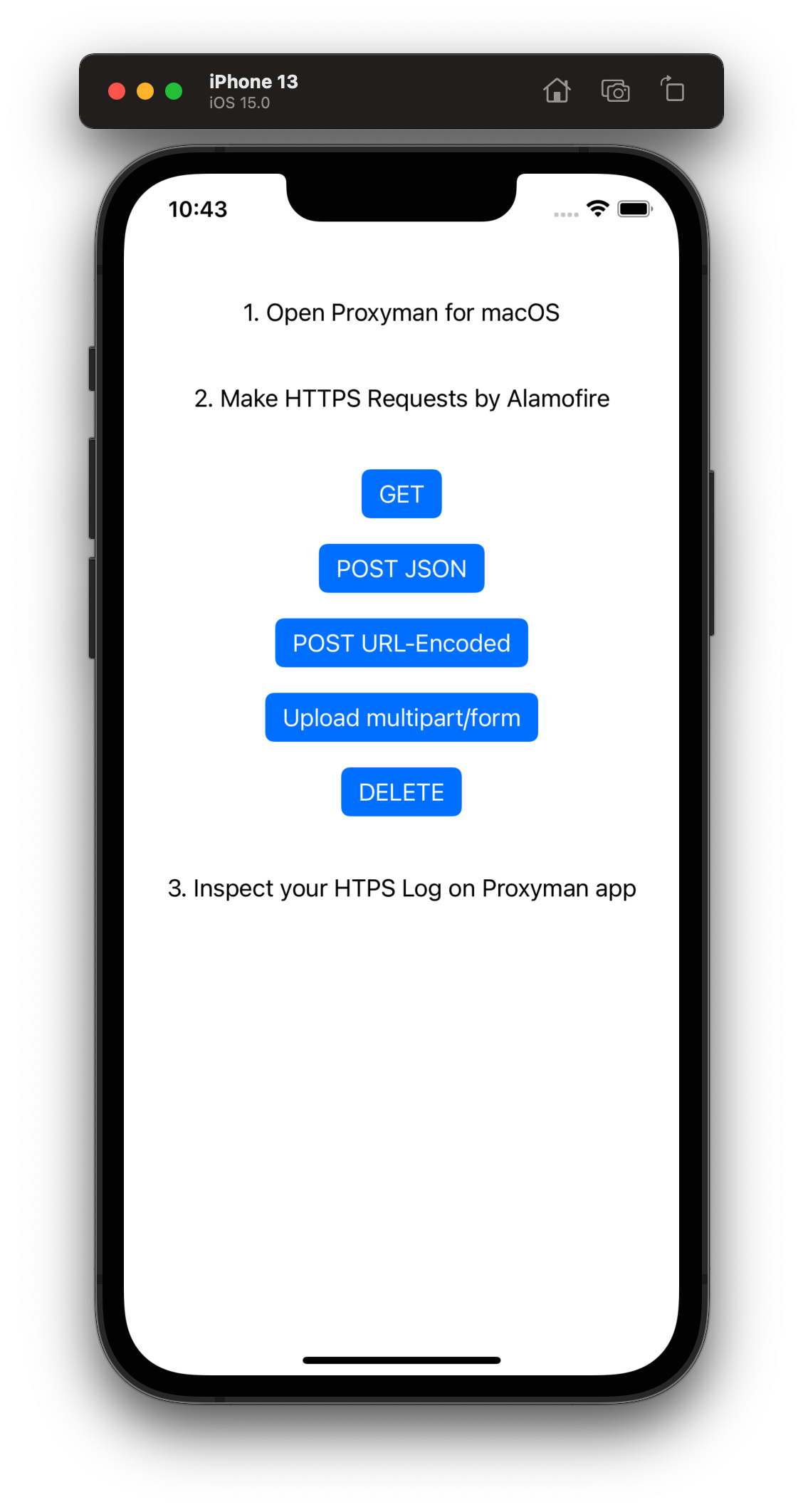
Atlantis provides a simple example that can demonstrate how to integrate and use Atlantis and Proxyman. Please follow the following steps:
- Open Proxyman for macOS
- Open iOS Project at
Example/Atlantis-Example-App.xcodeproj - Start the project with any iPhone/iPad Simulator
- Click on buttons on the main screen
- Back to Proxyman app and inspect your HTTPS Request/Response.
By default, if your iOS app uses Apple's Networking classes (e.g. URLSession) or using popular Networking libraries (e.g. Alamofire and AFNetworking) to make an HTTP Request, Atlantis will work OUT OF THE BOX.
However, if your app doesn't use any one of them, Atlantis is not able to automatically capture the network traffic.
To resolve it, Atlantis offers certain functions to help you manually* add your Request and Response that will present on the Proxyman app as usual.
1. My app uses C++ Network library and doesn't use URLSession, NSURLSession, or any iOS Networking library
You can construct the Request and Response for Atlantis from the following func
/// Handy func to manually add Atlantis' Request & Response, then sending to Proxyman for inspecting
/// It's useful if your Request & Response are not URLRequest and URLResponse
/// - Parameters:
/// - request: Atlantis' request model
/// - response: Atlantis' response model
/// - responseBody: The body data of the response
public class func add(request: Request,
response: Response,
responseBody: Data?) {- Example:
@IBAction func getManualBtnOnClick(_ sender: Any) {
// Init Request and Response
let header = Header(key: "X-Data", value: "Atlantis")
let jsonType = Header(key: "Content-Type", value: "application/json")
let jsonObj: [String: Any] = ["country": "Singapore"]
let data = try! JSONSerialization.data(withJSONObject: jsonObj, options: [])
let request = Request(url: "https://proxyman.io/get/data", method: "GET", headers: [header, jsonType], body: data)
let response = Response(statusCode: 200, headers: [Header(key: "X-Response", value: "Internal Error server"), jsonType])
let responseObj: [String: Any] = ["error_response": "Not FOund"]
let responseData = try! JSONSerialization.data(withJSONObject: responseObj, options: [])
// Add to Atlantis and show it on Proxyman app
Atlantis.add(request: request, response: response, responseBody: responseData)
}You can construct the unary Request and Response from GRPC models via the interceptor pattern that is provided by grpc-swift and leverage this to get a complete log of your calls.
Here is an example for an AtlantisInterceptor
import Atlantis
import Foundation
import GRPC
import NIO
import NIOHPACK
import SwiftProtobuf
extension HPACKHeaders {
var atlantisHeaders: [Header] { map { Header(key: $0.name, value: $0.value) } }
}
public class AtlantisInterceptor<Request: Message, Response: Message>: ClientInterceptor<Request, Response> {
private struct LogEntry {
let id = UUID()
var path: String = ""
var started: Date?
var request: LogRequest = .init()
var response: LogResponse = .init()
}
private struct LogRequest {
var metadata: [Header] = []
var messages: [String] = []
var ended = false
}
private struct LogResponse {
var metadata: [Header] = []
var messages: [String] = []
var end: (status: GRPCStatus, metadata: String)?
}
private var logEntry = LogEntry()
override public func send(_ part: GRPCClientRequestPart<Request>,
promise: EventLoopPromise<Void>?,
context: ClientInterceptorContext<Request, Response>)
{
logEntry.path = context.path
if logEntry.started == nil {
logEntry.started = Date()
}
switch context.type {
case .clientStreaming, .serverStreaming, .bidirectionalStreaming:
streamingSend(part, type: context.type)
case .unary:
unarySend(part)
}
super.send(part, promise: promise, context: context)
}
private func streamingSend(_ part: GRPCClientRequestPart<Request>, type: GRPCCallType) {
switch part {
case .metadata(let metadata):
logEntry.request.metadata = metadata.atlantisHeaders
case .message(let messageRequest, _):
Atlantis.addGRPCStreaming(id: logEntry.id,
path: logEntry.path,
message: .data((try? messageRequest.jsonUTF8Data()) ?? Data()),
success: true,
statusCode: 0,
statusMessage: nil,
streamingType: type.streamingType,
type: .send,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
case .end:
logEntry.request.ended = true
switch type {
case .unary, .serverStreaming, .bidirectionalStreaming:
break
case .clientStreaming:
Atlantis.addGRPCStreaming(id: logEntry.id,
path: logEntry.path,
message: .string("end"),
success: true,
statusCode: 0,
statusMessage: nil,
streamingType: type.streamingType,
type: .send,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
}
}
}
private func unarySend(_ part: GRPCClientRequestPart<Request>) {
switch part {
case .metadata(let metadata):
logEntry.request.metadata = metadata.atlantisHeaders
case .message(let messageRequest, _):
logEntry.request.messages.append((try? messageRequest.jsonUTF8Data())?.prettyJson ?? "")
case .end:
logEntry.request.ended = true
}
}
override public func receive(_ part: GRPCClientResponsePart<Response>, context: ClientInterceptorContext<Request, Response>) {
logEntry.path = context.path
switch context.type {
case .unary:
unaryReceive(part)
case .bidirectionalStreaming, .serverStreaming, .clientStreaming:
streamingReceive(part, type: context.type)
}
super.receive(part, context: context)
}
private func streamingReceive(_ part: GRPCClientResponsePart<Response>, type: GRPCCallType) {
switch part {
case .metadata(let metadata):
logEntry.response.metadata = metadata.atlantisHeaders
case .message(let messageResponse):
Atlantis.addGRPCStreaming(id: logEntry.id,
path: logEntry.path,
message: .data((try? messageResponse.jsonUTF8Data()) ?? Data()),
success: true,
statusCode: 0,
statusMessage: nil,
streamingType: type.streamingType,
type: .receive,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
case .end(let status, _):
Atlantis.addGRPCStreaming(id: logEntry.id,
path: logEntry.path,
message: .string("end"),
success: status.isOk,
statusCode: status.code.rawValue,
statusMessage: status.message,
streamingType: type.streamingType,
type: .receive,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
}
}
private func unaryReceive(_ part: GRPCClientResponsePart<Response>) {
switch part {
case .metadata(let metadata):
logEntry.response.metadata = metadata.atlantisHeaders
case .message(let messageResponse):
logEntry.response.messages.append((try? messageResponse.jsonUTF8Data())?.prettyJson ?? "")
case .end(let status, _):
Atlantis.addGRPCUnary(path: logEntry.path,
requestObject: logEntry.request.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
responseObject: logEntry.response.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
success: status.isOk,
statusCode: status.code.rawValue,
statusMessage: status.message,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
}
}
override public func errorCaught(_ error: Error, context: ClientInterceptorContext<Request, Response>) {
logEntry.path = context.path
switch context.type {
case .unary, .bidirectionalStreaming, .serverStreaming, .clientStreaming:
Atlantis.addGRPCUnary(path: logEntry.path,
requestObject: logEntry.request.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
responseObject: logEntry.response.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
success: false,
statusCode: GRPCStatus(code: .unknown, message: "").code.rawValue,
statusMessage: error.localizedDescription,
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
}
super.errorCaught(error, context: context)
}
override public func cancel(promise: EventLoopPromise<Void>?, context: ClientInterceptorContext<Request, Response>) {
logEntry.path = context.path
switch context.type {
case .unary, .bidirectionalStreaming, .serverStreaming, .clientStreaming:
Atlantis.addGRPCUnary(path: logEntry.path,
requestObject: logEntry.request.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
responseObject: logEntry.response.messages.joined(separator: "\n").data(using: .utf8),
success: false,
statusCode: GRPCStatus(code: .cancelled, message: nil).code.rawValue,
statusMessage: "canceled",
startedAt: logEntry.started,
endedAt: Date(),
HPACKHeadersRequest: logEntry.request.metadata,
HPACKHeadersResponse: logEntry.response.metadata)
}
super.cancel(promise: promise, context: context)
}
}
extension GRPCCallType {
var streamingType: Atlantis.GRPCStreamingType {
switch self {
case .clientStreaming:
return .client
case .serverStreaming:
return .server
case .bidirectionalStreaming:
return .server
case .unary:
fatalError("Unary is not a streaming type")
}
}
}
private extension Data {
var prettyJson: String? {
guard let object = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: self),
let data = try? JSONSerialization.data(withJSONObject: object, options: [.prettyPrinted]),
let prettyPrintedString = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) else {
return nil
}
return prettyPrintedString
}
}- Example:
public class YourInterceptorFactory: YourClientInterceptorFactoryProtocol {
func makeGetYourCallInterceptors() -> [ClientInterceptor<YourRequest, YourResponse>] {
[AtlantisInterceptor()]
}
}
// Your GRPC services that is generated from SwiftGRPC
private let client = NoteServiceServiceClient.init(channel: connectionChannel, interceptors: YourInterceptorFactory())Atlantis is capable of capturing the HTTP/HTTPS and WS/WSS traffic from your Swift Playground.
- Use Arena to generate a new Swift Playground with Atlantis. If you would like to add Atlantis to your existing Swift Playground, please follow this tutorial.
- Enable Swift Playground Mode
Atlantis.setIsRunningOniOSPlayground(true)
Atlantis.start()- Trust Proxyman self-signed certificate
- for macOS: You don't need to do anything if you've already installed & trusted Proxyman Certificate in Certificate Menu -> Install on this Mac.
- for iOS: Since iOS Playground doesn't start any iOS Simulator, it's impossible to inject the Proxyman Certificate. Therefore, we have to manually trust the certificate. Please use NetworkSSLProxying class to do it.
- Make an HTTP/HTTPS or WS/WSS and inspect it on the Proxyman app.
Atlantis uses Method Swizzling technique to swizzle certain functions of NSURLSession that enables Atlantis captures HTTP/HTTPS traffic on the fly.
Then it sends to Proxyman app for inspecting later.
As soon as your iOS app (Atlantis is enabled) and the Proxyman macOS app are the same local network, Atlantis could discover the Proxyman app by using Bonjour Service. After the connection is established, Atlantis will send the data via Socket.
It's completely safe since your data is locally transferred between your iOS app and the Proxyman app, no Internet is required. All traffic logs are captures and send to the Proxyman app for inspecting on the fly.
Atlantis and Proxyman app do not store any of your data on any server.
- All HTTP/HTTPS traffic from your iOS apps, that integrate the Atlantis framework
- Your iOS app name, bundle identifier, and small size of the logo
- iOS devices/simulators name and device models.
All the above data are not stored anywhere (except in the memory). It will be wiped out as soon as you close the app.
They are required to categorize the traffic on the Proxyman app by project and device name. Therefore, it's easier to know where the request/response comes from.
For some reason, Bonjour service might not be able to find Proxyman app.
=> Make sure your iOS devices and the Mac are in the same Wifi Network or connect to your Mac with USB Cable
=> Please use Atlantis.start(hostName: "_your_host_name") version to explicitly tell Atlantis connect to your Mac.
Atlantis is built for inspecting the Network, not debugging purpose. If you would like to use Debugging Tools, please consider using normal HTTP Proxy
- FLEX and maintainer team: https://github.com/FLEXTool/FLEX
- @yagiz from Bagel project: https://github.com/yagiz/Bagel
Atlantis is released under the Apache-2.0 License. See LICENSE for details.