Unidirectional Data Flow in Swift - inspired by Redux and NgRx.
Based on Combine - ideal for use with SwiftUI.



When developing apps, it can quickly become difficult to keep track of the flow of data. Data flows in multiple directions and can easily become inconsistent with Multiple Sources of Truth.
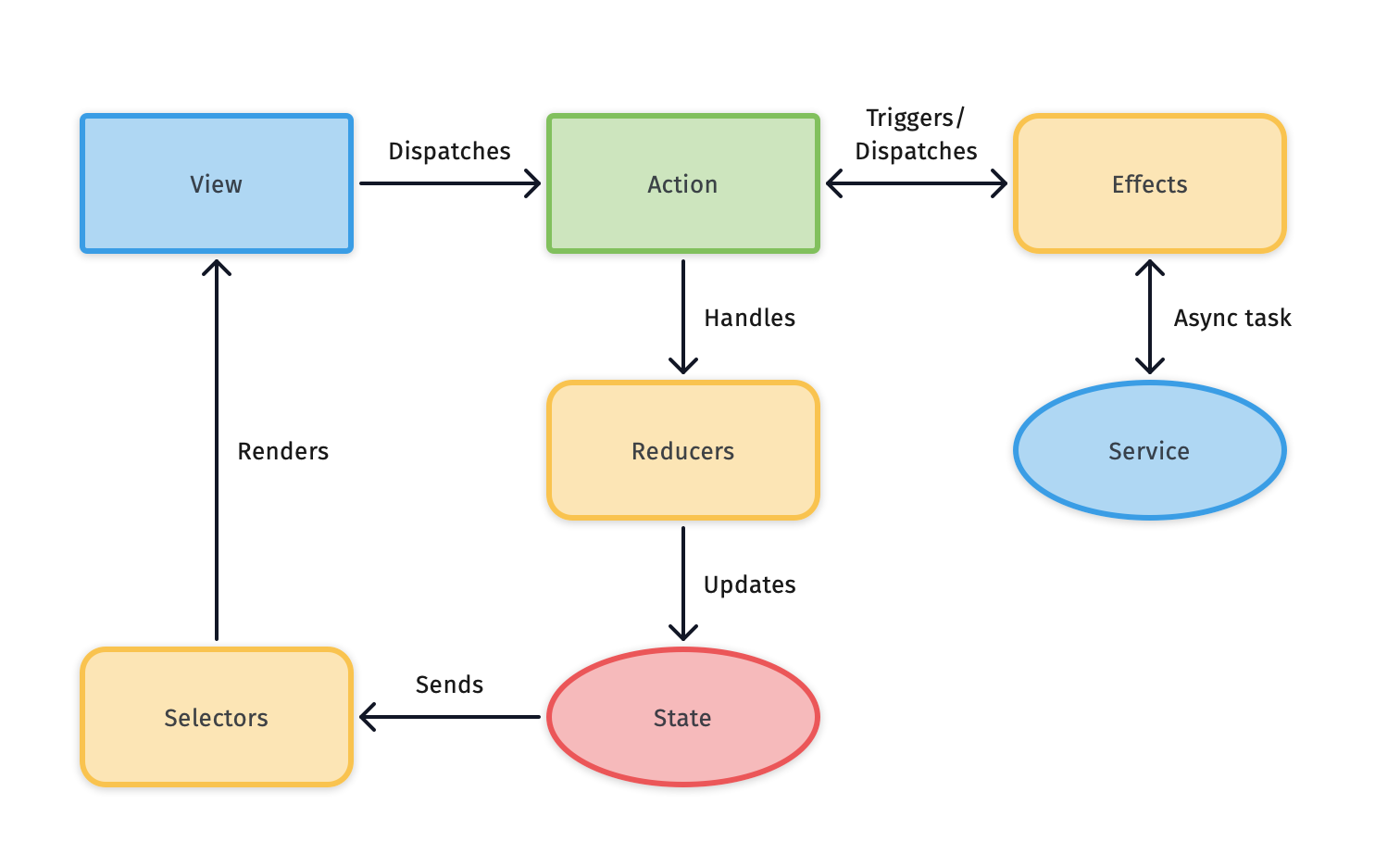
With Fluxor, data flows in only one direction, there is only one Single Source of Truth, updates to the state are done with pure functions, the flow in the app can easily be followed, and all the individual parts can be unit tested separately.
Fluxor is made up from the following types:
Storecontains an immutable state (the Single Source of Truth).Actions are dispatched on the Store to update the state.Reducers gives the Store a new state based on the Actions dispatched.Selectors selects (and eventually transform) part(s) of the state to use (eg. in views).Effects gets triggered by Actions, and can perform async task which in turn can dispatch new Actions.Interceptors intercepts every dispatched Action and state change for easier debugging.
Fluxor can be installed as a dependency to your project using Swift Package Manager, by simply adding https://github.com/FluxorOrg/Fluxor.git.
- iOS 13.0+ / macOS 10.15+ / tvOS 13.0+ / watchOS 6.0+ / Linux
- Xcode 11.4+ / Swift 5.2+
As a minimum, an app using Fluxor will need a Store, an Action, a Reducer, a Selector and a state.
Here is a setup where firing the IncrementAction (1) will increment the counter (2) in AppState (3), and when selecting with the counterSelector (4) on the Store will publish the counter everytime the state changes (5).
import Combine
import Fluxor
import Foundation
// 3
struct AppState {
var counter: Int
}
// 1
struct IncrementAction: Action {
let increment: Int
}
// 4
let counterSelector = Selector(keyPath: \AppState.counter)
let store = Store(initialState: AppState(counter: 0))
store.register(reducer: Reducer(
ReduceOn(IncrementAction.self) { state, action in
state.counter += action.increment // 2
}
))
let cancellable = store.select(counterSelector).sink {
print("Current count: \($0)") // 5
}
store.dispatch(action: IncrementAction(increment: 42))
// Will print out "Current count: 42"The above example is a simple use case, where an Action is dispatched and the state is updated by a Reducer. In cases where something should happen when an Action is dispatched (eg. fetching data from the internet or some system service), Fluxor provides Effects.
Effects are registered in the Store and will receive all Actions dispatched. An Effect will in most cases be a Publisher mapped from the dispatched Action - the mapped Action will be dispatched on the Store.
Alternatively an Effect can also be a Cancellable when it don't need to have an Action dispatched.
import Combine
import Fluxor
import Foundation
class TodosEffects: Effects {
typealias Environment = AppEnvironment
let fetchTodos = Effect<Environment>.dispatchingOne { actions, environment in
actions.ofType(FetchTodosAction.self)
.flatMap { _ in
environment.todoService.fetchTodos()
.map { DidFetchTodosAction(todos: $0) }
.catch { _ in Just(DidFailFetchingTodosAction(error: "An error occurred.")) }
}
.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
}If read-only access to all Actions dispatched and state changes is needed, an Interceptor can be used. Interceptor is just a protocol, and when registered in the Store, instances of types conforming to this protocol will receive a callback everytime an Action is dispatched.
Fluxor comes with two implementations of Interceptor:
PrintInterceptorfor printingActions and state changes to the log.TestInterceptorto help assert that specificActions was dispatched in unit tests.
Fluxor comes with packages, to make it easier to use it with SwiftUI and for testing apps using Fluxor.
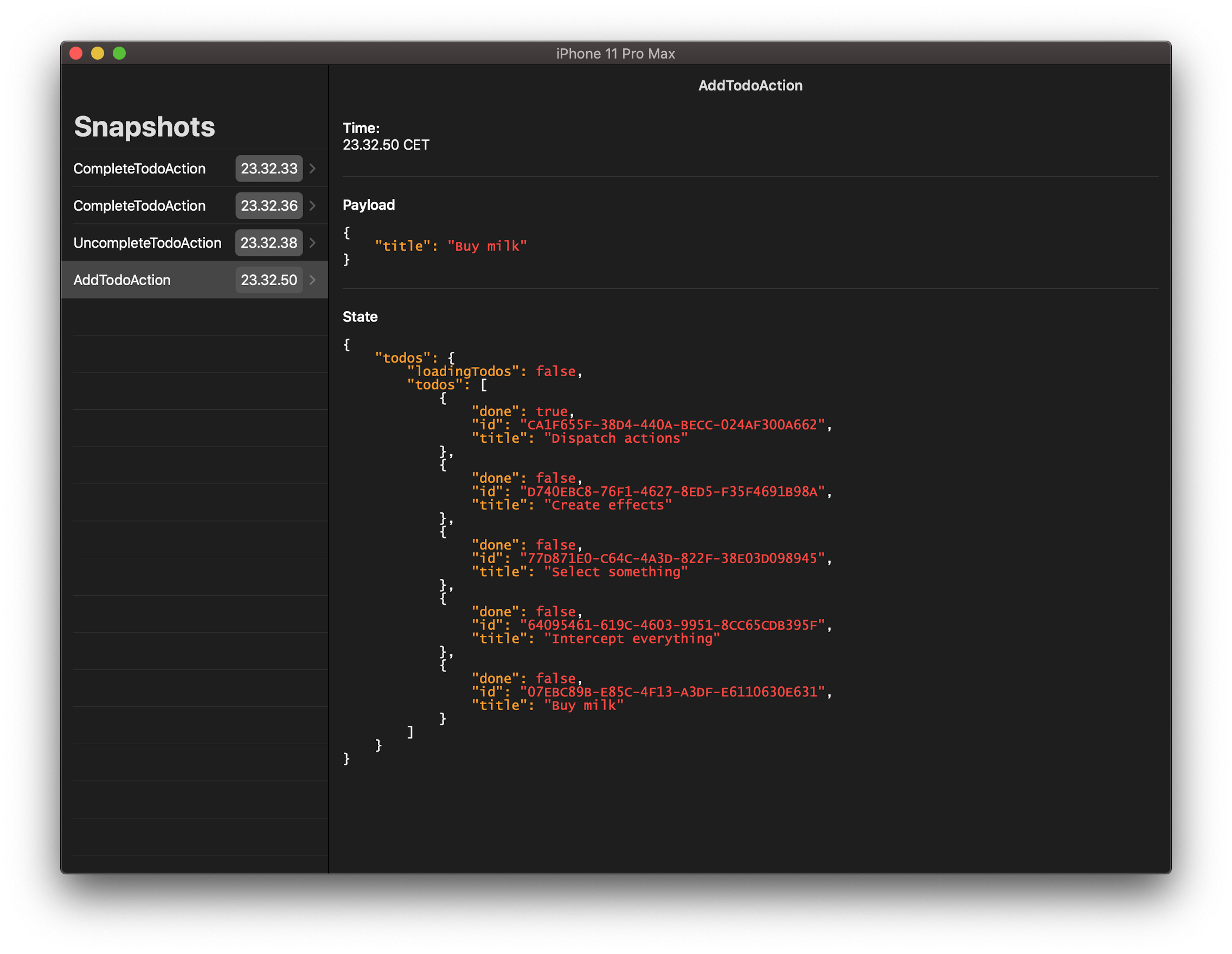
Fluxor has a companion app, FluxorExplorer, which helps when debugging apps using Fluxor. FluxorExplorer lets you look through the dispatched Actions and state changes, to debug the data flow of the app.
FluxorExplorer is available on the App Store but also available as open source.
To learn more about how to use FluxorExplorer, go to the repository for the app.